Granulation Machine

Would you like us to granulate your material?
Granulation Machine Services
Chemical
Mining
Agriculture
Fertilizer
Pharmaceutical
Food
Biomass
Institutions
Parameters
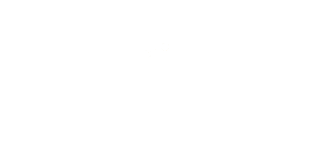
Typical Flowchart
Granulation Method
Material Particle Size
Desired Product Size
Moisture Content
Binder Type
Binder Concentration
Formulation Ingredients
Shear Forces
Rotational Frequency
Desired Characteristics
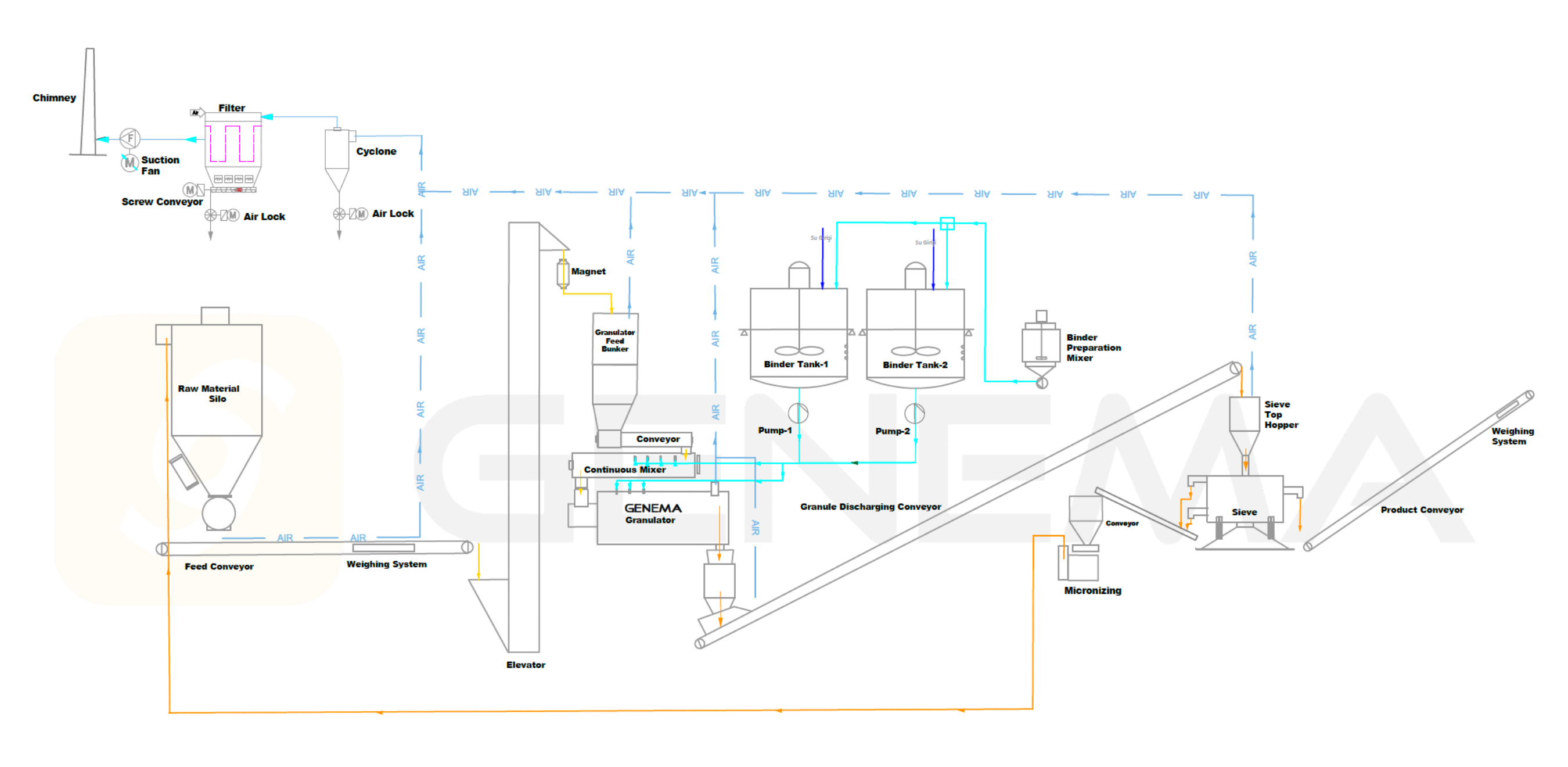
Pelletizing/Granulation Plant Manufacturing

Equipments in granulation plants must work in harmony like a philharmonic orchestra. Because the design and sizing of the equipment to be used before and after granulation directly affects the success of the process. The raw materials to be fed into the system can be powder or coarser materials. In the case of coarser materials, they are usually ground by means of a crusher at the inlet. There are also some special cases. In fertilizer plants, for example, organic sources usually arrive at the facility with high humidity. In this case, it is difficult to break the moist material. For this reason, the organic material is first dried and then crushed.
Equipments in granulation plants must work in harmony like a philharmonic orchestra.
After the granulation step in the granulation machine, drying/calcination and cooling of the granules under appropriate conditions are also important to maintain granular strength. Therefore, it is not an option but a necessity for the manufacturer to be capable of designing and manufacturing the entire system. In general terms, the operations in a granulation plant are summarized below:
Pre-Granulation Processes
Raw Material Preparation
Material preparation is the work of bringing raw materials to the appropriate moisture and grain size. In most cases, a maxi drying system will be an efficient and practical choice to reduce the moisture content of raw materials.
- The raw material stock area stores materials in favorable conditions.
- The drying system reduces the moisture content of moist materials.
- The grinding system turns large particles into fine powder.
- Silos, bunkers or big-bags provide storage after preparation.
Dosing
Dosing is the work of feeding raw materials to the system in appropriate ratios with appropriate systems.
In some scenarios:
- The operator hangs the big-bags of powdered raw material on the big-bag unloading unit with the help of a forklift.
- In line with the desired formulation, the big-bag unloading units discharge the raw materials into the feeder screw.
In some scenarios (e.g. NPK plants):
- The operator transfers the powdered raw materials to the feed hoppers with a bucket.
- The feed hopper transfers the raw materials to a feed conveyor in line with the specified formulation.
Mixing
This process is the mixing of raw materials to create a homogeneous mixture. The quality of the mixture directly affects the quality of the final granular product. This is especially critical when the formulation includes components in very small quantities but which have a significant impact on the final product’s properties.
- Suitable conveying components transport the raw materials to the mixer.
- Mixer feeding system feeds binders, diluents, surface conditioners etc. into the system before granulation.
- High-speed mixer technology reduces processing time and creates homogeneous mixtures.
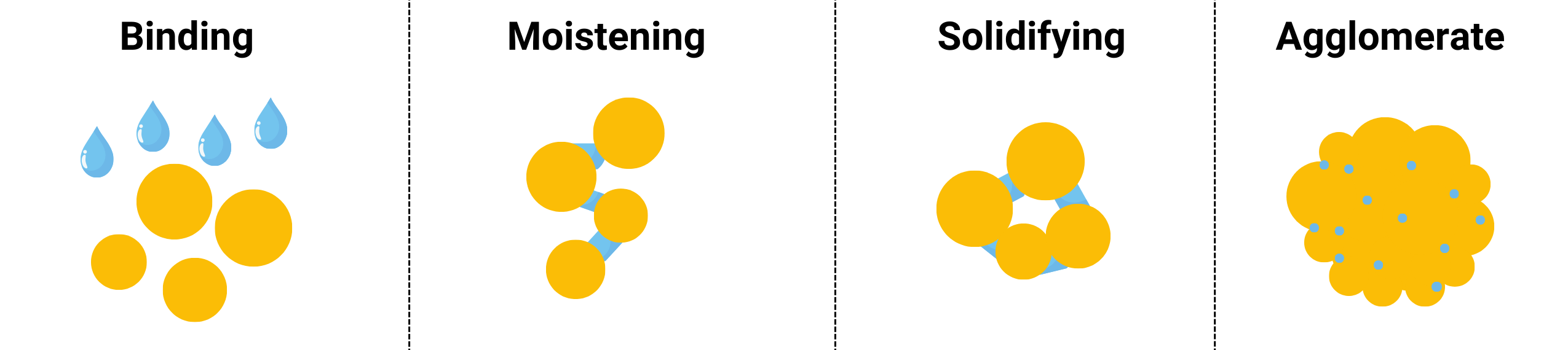
Granulation Process
Granulation
The granulation machine is the heart of the granulation plant. The importance of granule size varies by industries. For instance; in the chemical industry, granule size can affect reaction rates, efficiency and product purity. Especially for catalysts and reactive materials. Optimization of granule size ensures maximum reaction surface area and thus reaction efficiency. Fine granules increase the surface area, while very fine materials can cause agglomeration, which can reduce reaction efficiency. In the pharmaceutical industry, granule size directly affects the absorption rate, solubility and bioavailability of drugs. Generally, granule sizes 0.1-1 mm are preferred. In the food industry, granule size can have a direct impact on the texture, appearance and taste of the product. Granules produced for the fertilizer industry shall be suitable for use with agricultural tools such as ‘drill’. Generally, standard sizes of 2-4 mm are preferable, also niche micro-granules of 0.5-1.2 mm can be produced. Ultimately, the whole system must be custom-made to the needs.
- Speed-controlled elevator feeds the homogeneous mixture of raw materials and auxiliary materials into the granulator feeding hopper.
- Operator adjusts the process parameters according to the data obtained from the GENEMA test center.
- Process control system reports the data of the granulation operation simultaneously.
- Granulation machine forms homogeneous granules of the desired size.
- The data is stored in the central storage system for later use in optimization activities.
Post-Granulation Processes
Coating
Coating process, like the granulation process, is a multi-parameter operation that requires knowledge and experience. The granule coating process can be used for different purposes in different industries. For example, in the agricultural industry, seed coating can increase the germination rate. Fertilizer coating is important for the development of special slow-release products. Granular coating in the chemical industry can be important to keep the reactive properties of materials under control. Coated granules in the construction industry can provide both aesthetic appearance and resistance to UV radiation.
- Speed-controlled elevator feeds the granules into the coating machine feed hopper.
In some scenarios - Micro-dosing system feeds the coating machine at ppm level. The dosing system can feed liquid or powder.
In some scenarios - Macro-dosing system feeds higher quantities of coating material into the coating machine. In some applications, the coating system is designed to first heat and then feed high viscosity coating materials. (e.g wax type)
Drying/Calcination
The drying/calcination operation is very important to ensure that the strength of the granules is maintained. The drying/calcination equipment to be used should not damage, even improve the granule structure.
- The granule drying/calcining machine reduces the granule moisture to the desired level.
- The granule drying/calcining machine provides heat energy from natural gas, LNG or solid fuel in accordance with the infrastructure.
Cooling
Cooling the granules after drying is also a critical step. Because above all, the cooling process prevents the granules from deforming. This helps to maintain the stability of the granular product. In addition, the raw materials used in the granulation process may contain components that can cause chemical reactions. High temperatures can accelerate these reactions and lead to undesirable product properties. The cooling process helps to prevent such reactions.
- The granule cooling machine is located directly below the dryer.
- Or the feeding conveyor feeds the granules discharged from the dryer to the cooling machine.
Sieving
Granules formed during the granulation process can be of different sizes and may contain unwanted particles. The sieving operation separates these different sizes of granules and ensures that granules of the desired size and quality are selected. This improves the homogeneity and quality of the final product.
- The sieve usually separates the granules into 3 fractions according to their sizes.
- In some cases, sieved materials are fed back into the system.
- In some cases, the crusher of the process grinds the material above the screen and feeds it back into the system.
Packing
It is the most enjoyable unit to watch in the plant because the product is now ready to sale. To give a brief overview: The pharmaceutical, chemical and food industries generally prefer packaging machines with smaller dosing systems, while the mining and fertilizer industries prioritize high volume dosing.
- The automatic weighing packaging system discharges the product into the sack/pack.
- The operator can sew by hand after the sack filling is completed, or this process can be automated via a conveyor and automatic sewing machine.
- In some cases (e.g. pharmaceuticals) the packaging machine fills in a way that prevents contamination.
Ultimately, a successful granulation operation depends on the entire system as well as the granulation machine.
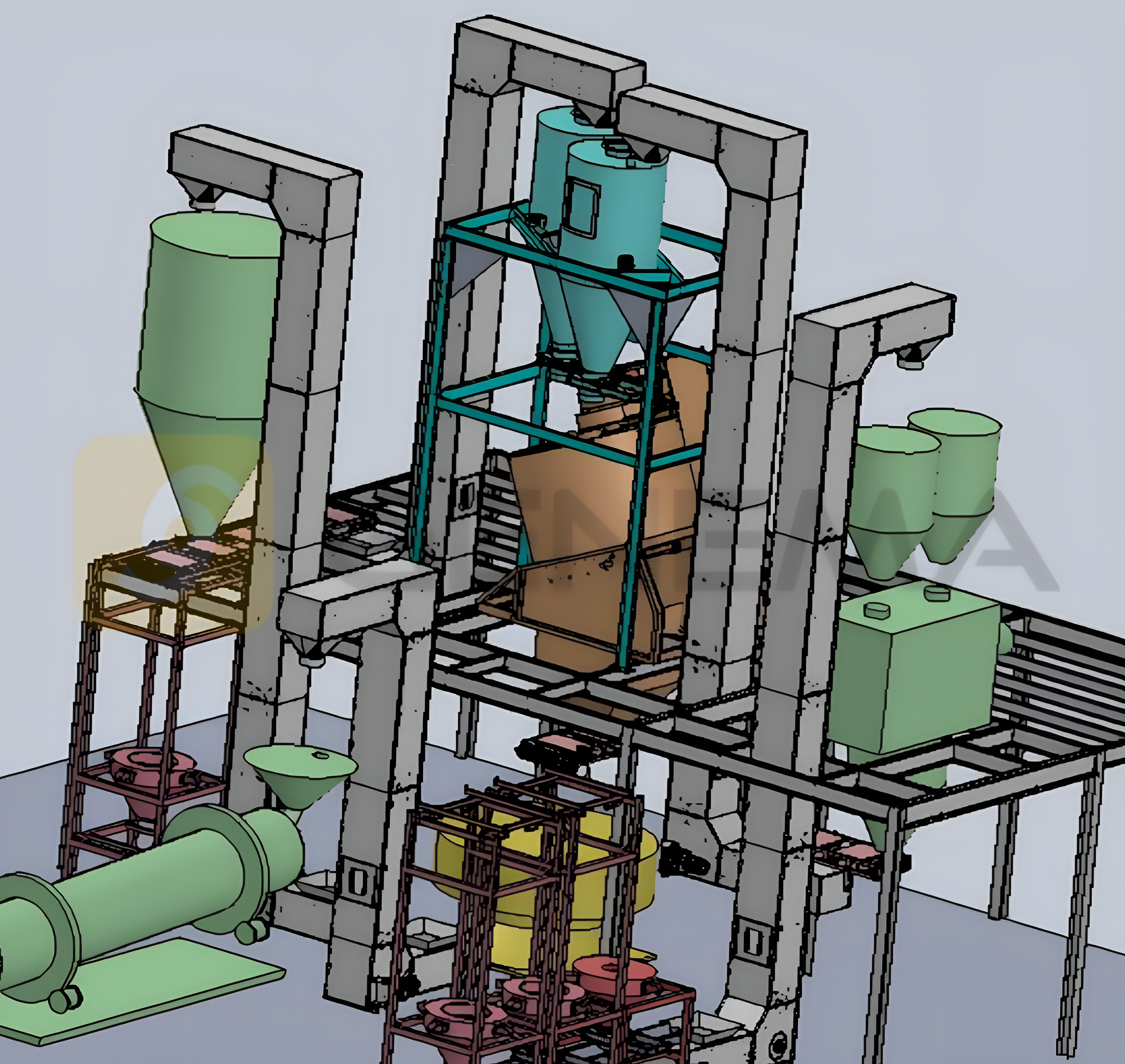

Raw Material Storage Units
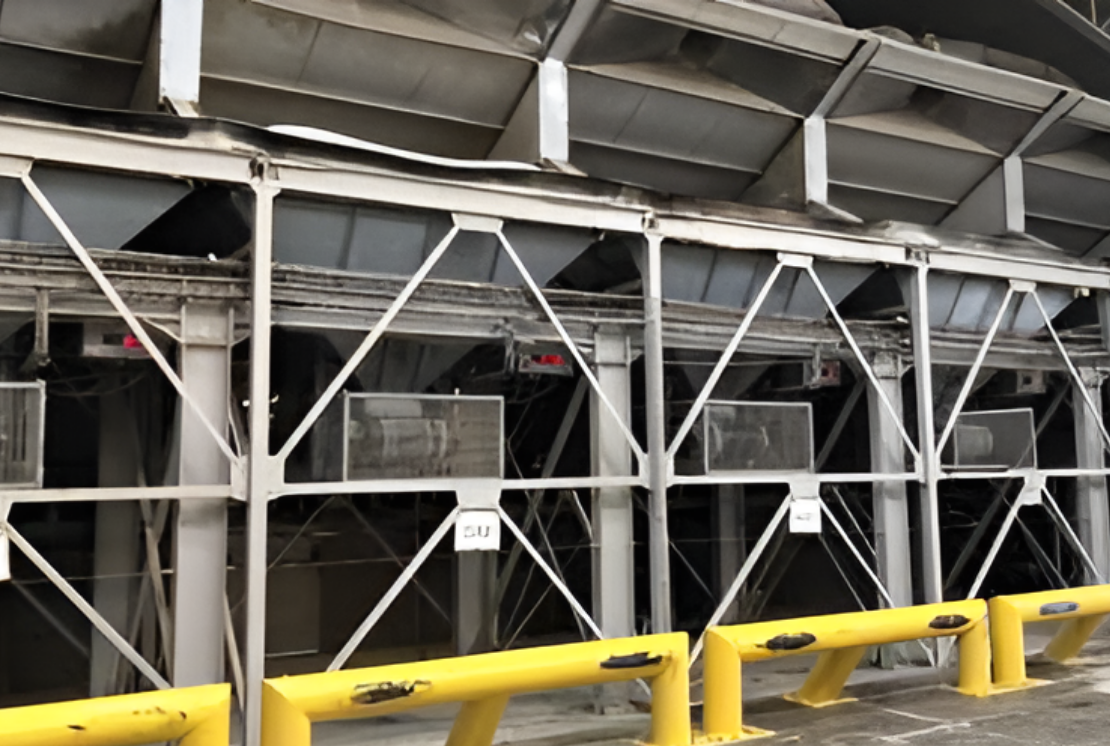

Dosing Unit

Industrial Mixer
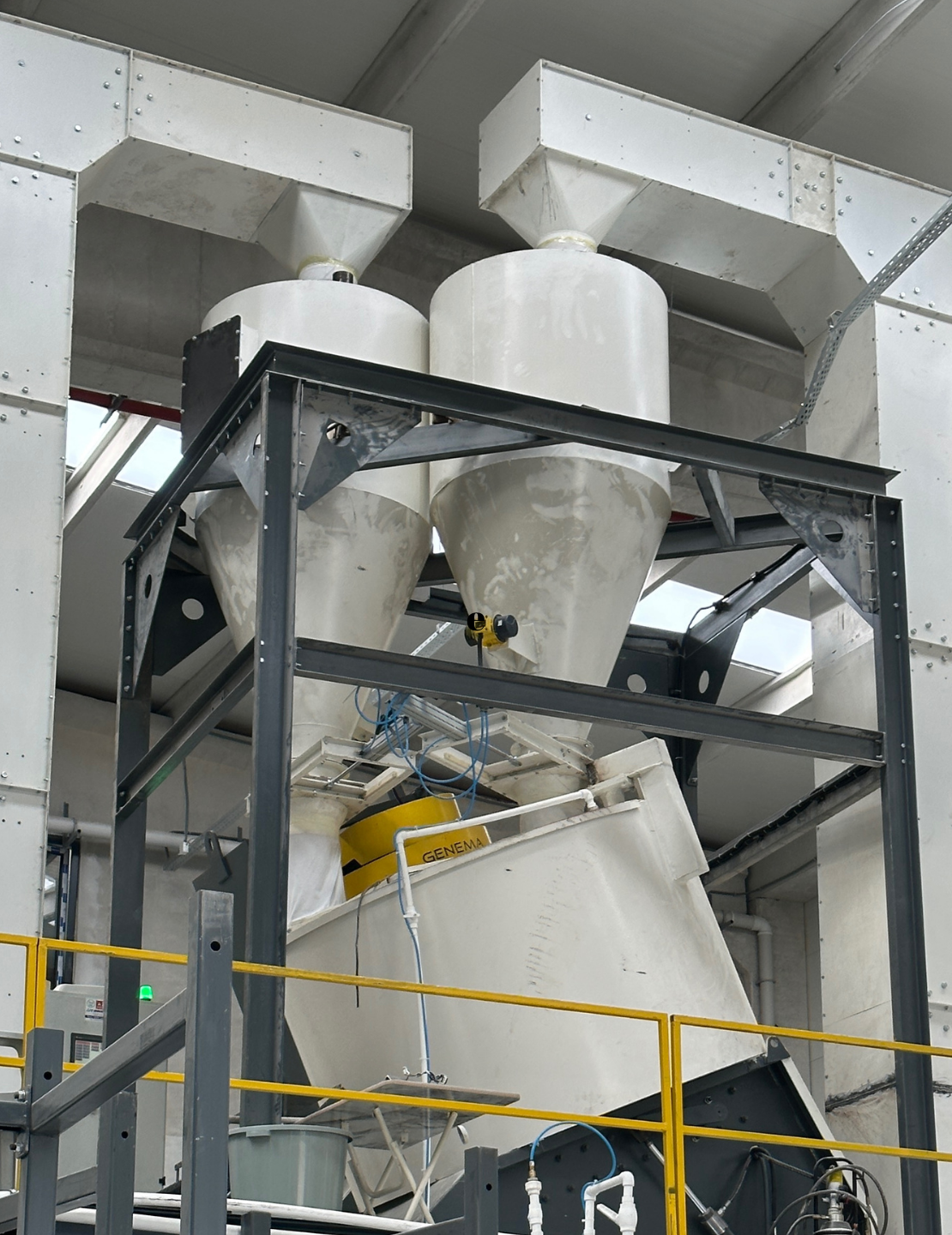

Turbo Granulation Machine
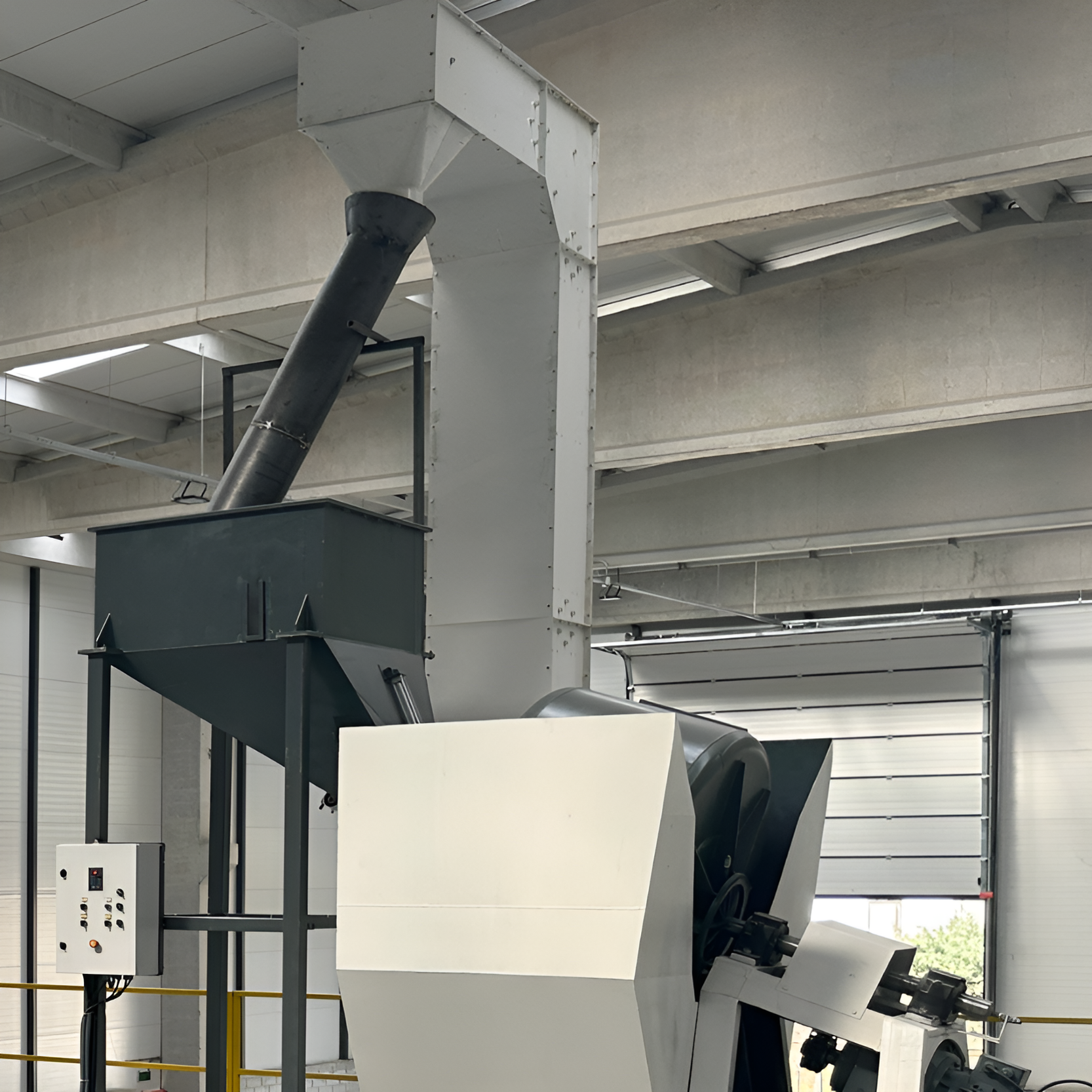

Coating Machine

Calcination Furnace
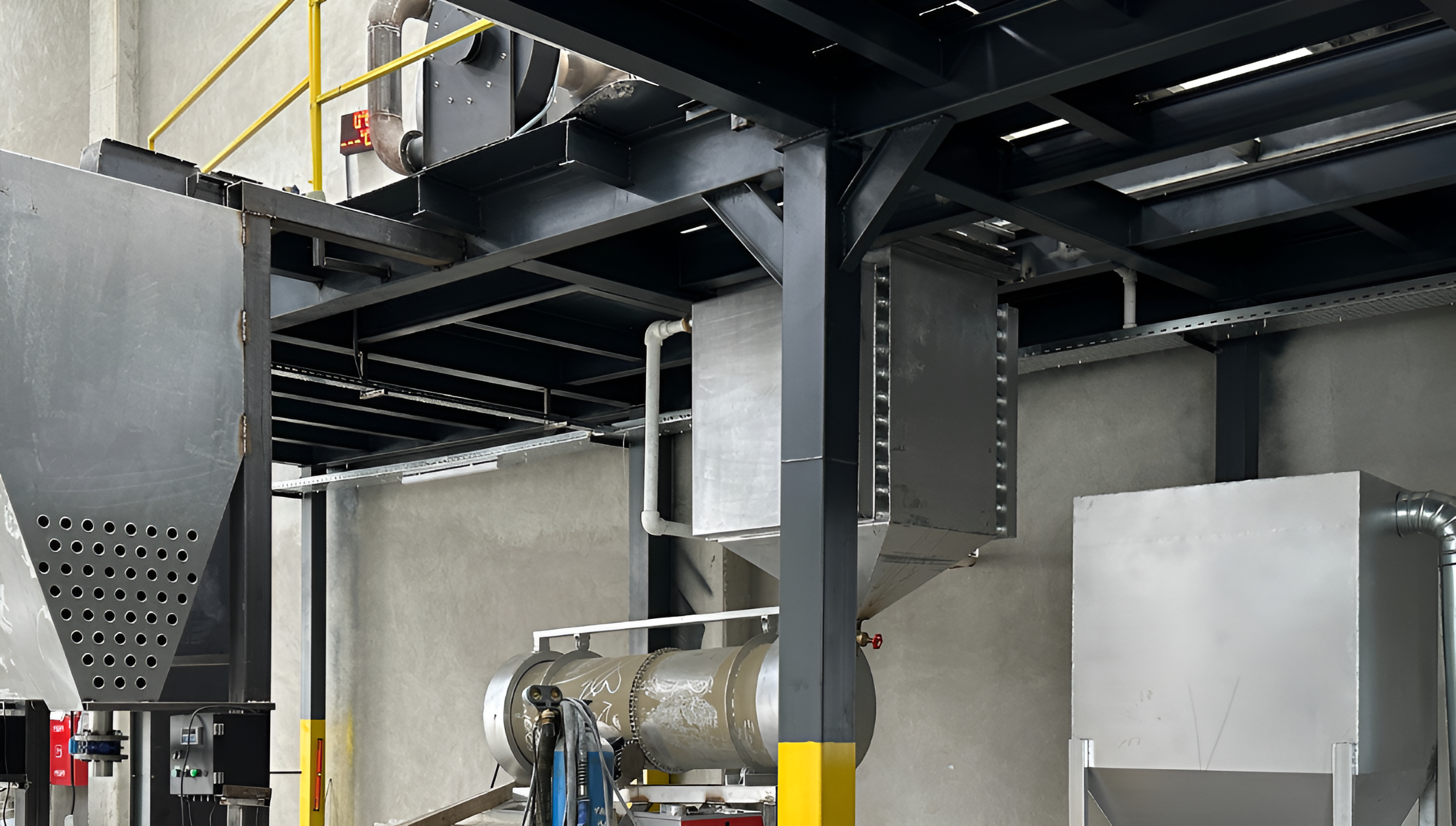

Industrial Cooling Process
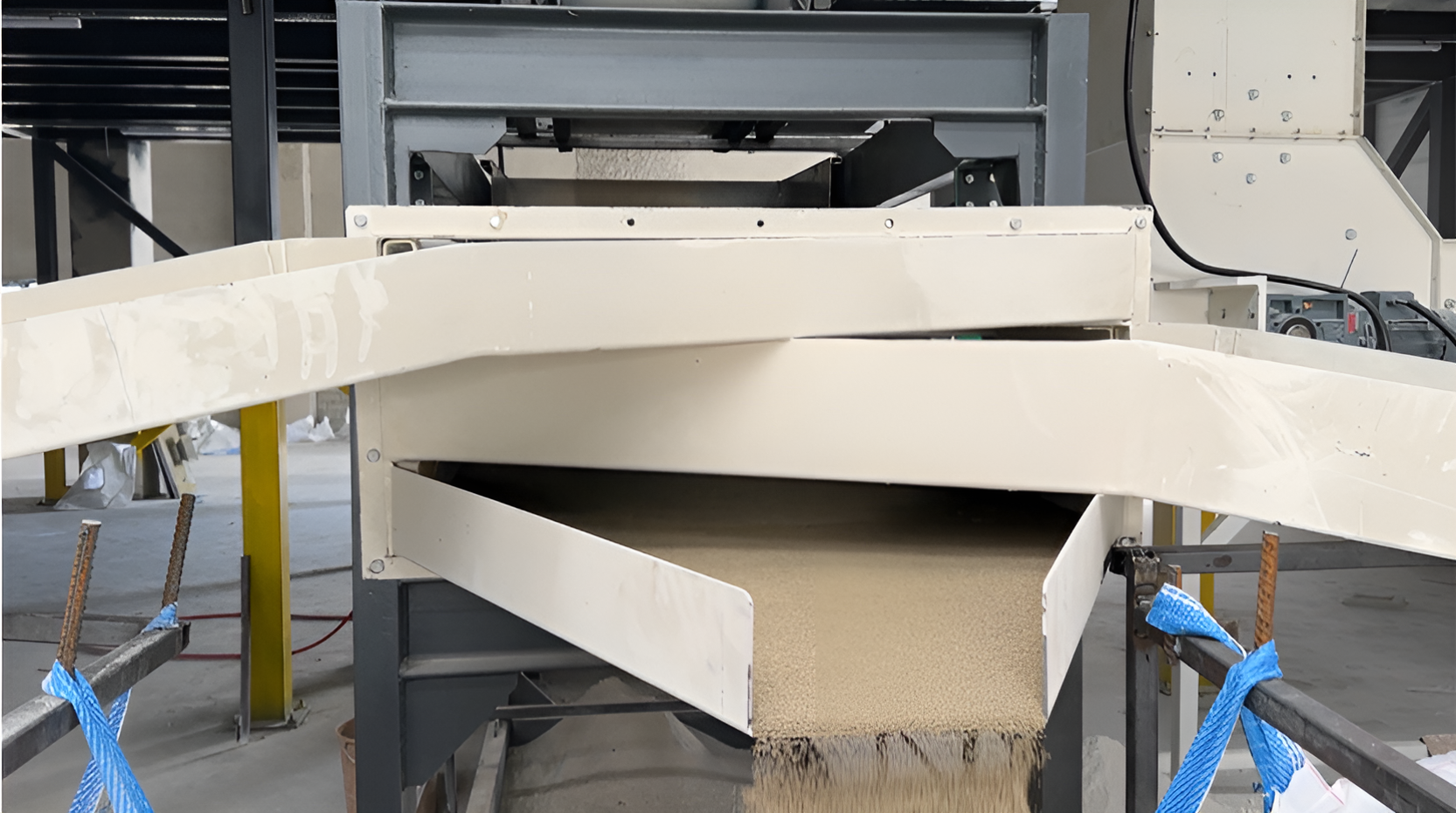

Sieving Machine

Packing Machine