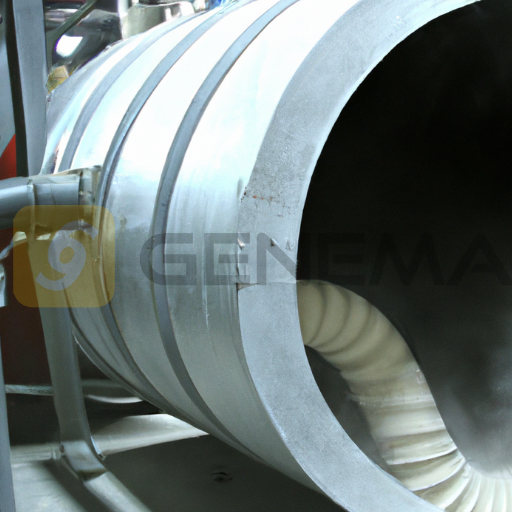
Calcination furnace, which is an industrial processing equipment, heats materials to high temperatures in order to cause chemical reactions or remove moisture and other impurities.
These furnaces have a wide range of applications, including:
Cement production: Calcination furnaces heat limestone and clay to produce cement. Operators heat the materials to temperatures of up to 1,450°C to produce clinker, which they then grind into cement.
Metal production: Calcination furnaces assist in the production of metals such as aluminum and steel. The furnaces heat ore and other raw materials to extract the metal and remove impurities.
Chemical production: Calcination furnaces assist in the production of a variety of chemicals, including soda ash, lime, and sulfuric acid. The furnaces heat raw materials to produce the desired chemical.
Waste treatment: Calcination furnaces help with the treatment of waste materials, such as municipal solid waste and hazardous waste. The furnaces burn the waste materials to reduce their volume and destroy harmful contaminants.
Mineral processing: Calcinators assist in the processing of minerals such as gypsum and bauxite. The furnaces heat the minerals to remove moisture and other impurities.
Calcination Furnace Design
Designers create calcinators to operate at high temperatures and often equip them with advanced temperature control systems to ensure precise and consistent heating. These furnaces produce a wide range of materials and products for use in a variety of industries.
Designers must consider a number of parameters when designing a calcination furnace. These parameters include:
Temperature: The temperature of the furnace is an important design consideration because it determines the materials that can be processed and the chemical reactions that can occur. Calcination furnaces are typically designed to operate at temperatures ranging from 800°C to 1,500°C, depending on the application.
Heat transfer: The method of heat transfer used in the furnace is an important design consideration. Calcination furnaces may use conduction, convection, or radiation to transfer heat to the materials being processed.
Fuel type: The type of fuel used to power the furnace is an important design consideration. Calcination furnaces may use a variety of fuels, including natural gas, propane, coal, or wood.
Material of construction: The material of construction for the furnace is an important design consideration because it must be able to withstand the high temperatures and chemical reactions that occur during the calcination process. Common materials of construction include refractory brick, ceramic fiber, and stainless steel.
Process flow: The design of the calcination furnace must consider the flow of materials through the furnace and the type of equipment used to load and unload the materials. The furnace may include feeders, conveyors, and other process equipment to facilitate the movement of materials.
Safety: The design of the calcination furnace must consider the safety of the operators and the surrounding environment. The furnace may include safety features such as alarms, shutdown systems, and emergency shutdown systems.
Overall, the design of a calcination furnace is a complex process that requires careful consideration of a wide range of parameters in order to ensure that the furnace is efficient, effective, and safe.
Video: Calcination Application
Request for quotation form: Calcination Furnace Request Form (RFQ)